- Account Home
- Language
- News
- Products
-
Cases
By Service
- Help & Support
- Partners & Training
- About Us
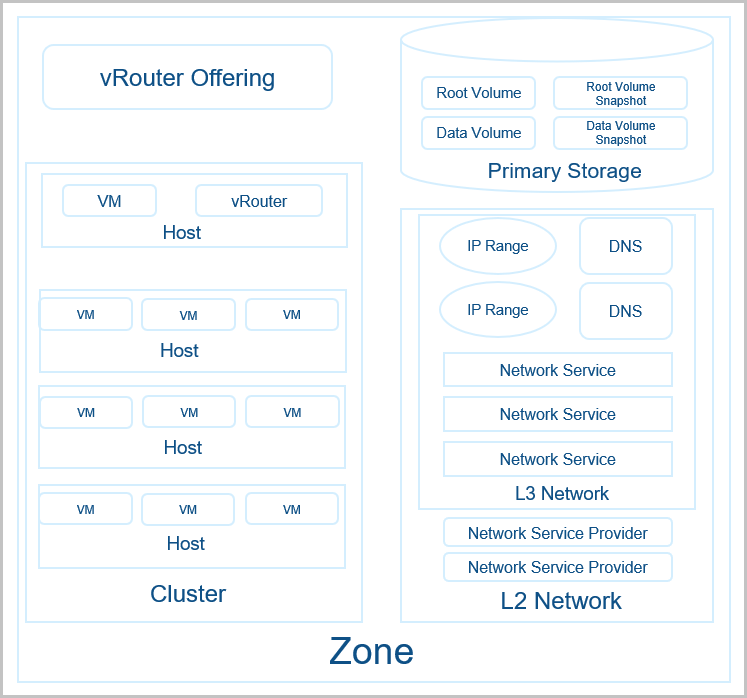
 Note: Relationship between primary storage and backup storage:
Note: Relationship between primary storage and backup storage:The following properties are common to almost all resources in ZStack:
Resources support full or partial Create, Read, Update, Delete (CRUD) operations.
A VM instance is a virtual machine instance running on a host. A VM instance has its own IP address to access a public network and run application services. VM instances are core components of ZStack.
Data volumes are mainly involved in the volume management.
Back to Top
Email Us
contact@zstack.ioEmail Us
contact@zstack.ioEmail Us
contact@zstack.ioThe download link is sent to your email address.
If you don't see it, check your spam folder, subscription folder, or AD folder. After receiving the email, click the URL to download the documentation.Thank you for using ZStack products and services.
Submit successfully.
We'll connect soon.Thank you for using ZStack products and services.