- Account Home
- Language
- News
- Products
-
Cases
By ServiceBy Solution
- Help & Support
- Partners & Training
- About Us
- 立即下载
HA Policy is a mechanism that ensures sustained and stable running of the business if VM instances are unexpectedly stopped or are errored because of errors occurring to compute, network, or storage resources associated with the VM instances. By enabling this feature, you can customize VM HA policies to ensure your business continuity and stability.
shutdown, poweroff, and halt commands in the VM OS.| Fault Scenario | Management Network Connectivity Status | Storage Network Connectivity Status | Business NIC Status | Fail Over |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Scenario A: Business NIC Fault | Normal | Normal | Abnormal | Enable/Disable |
| Scenario B: Storage Network Fault | Normal | Abnormal | Normal | Enable/Disable |
| Scenarios C: Storage Network and Business NIC Fault | Normal | Abnormal | Abnormal | Set as false if both the scenario A and B have the failover policy set as false. Set as true if either of the scenario A or B has the failover policy set as true. |
| Scenario D: Management Network Fault | Abnormal | Normal | Normal | Disable. The failover cannot be enabled in this scenario. |
 Note: The failover policies take effect on VM instances whose HA modes are set as NeverStop only.
Note: The failover policies take effect on VM instances whose HA modes are set as NeverStop only.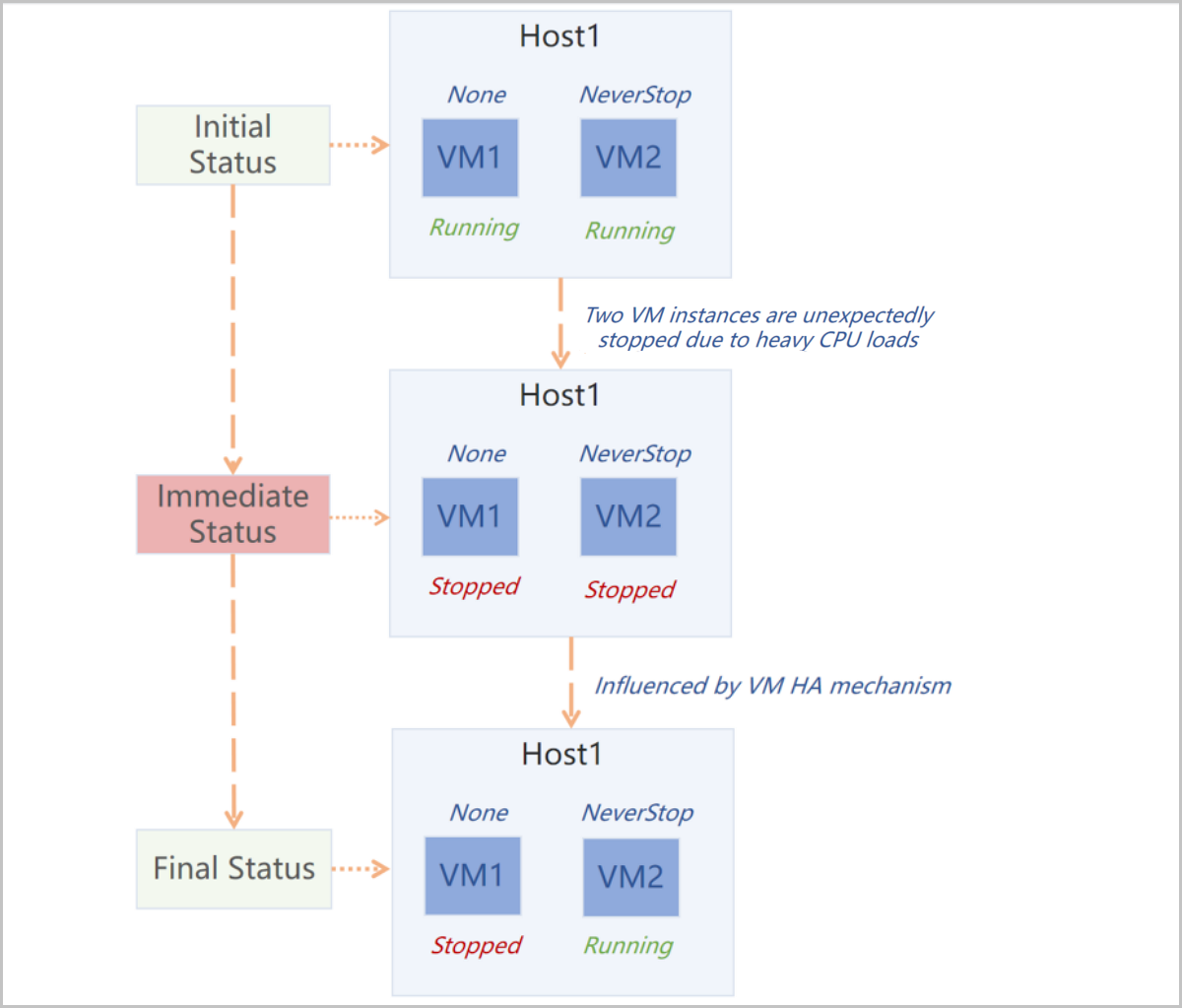
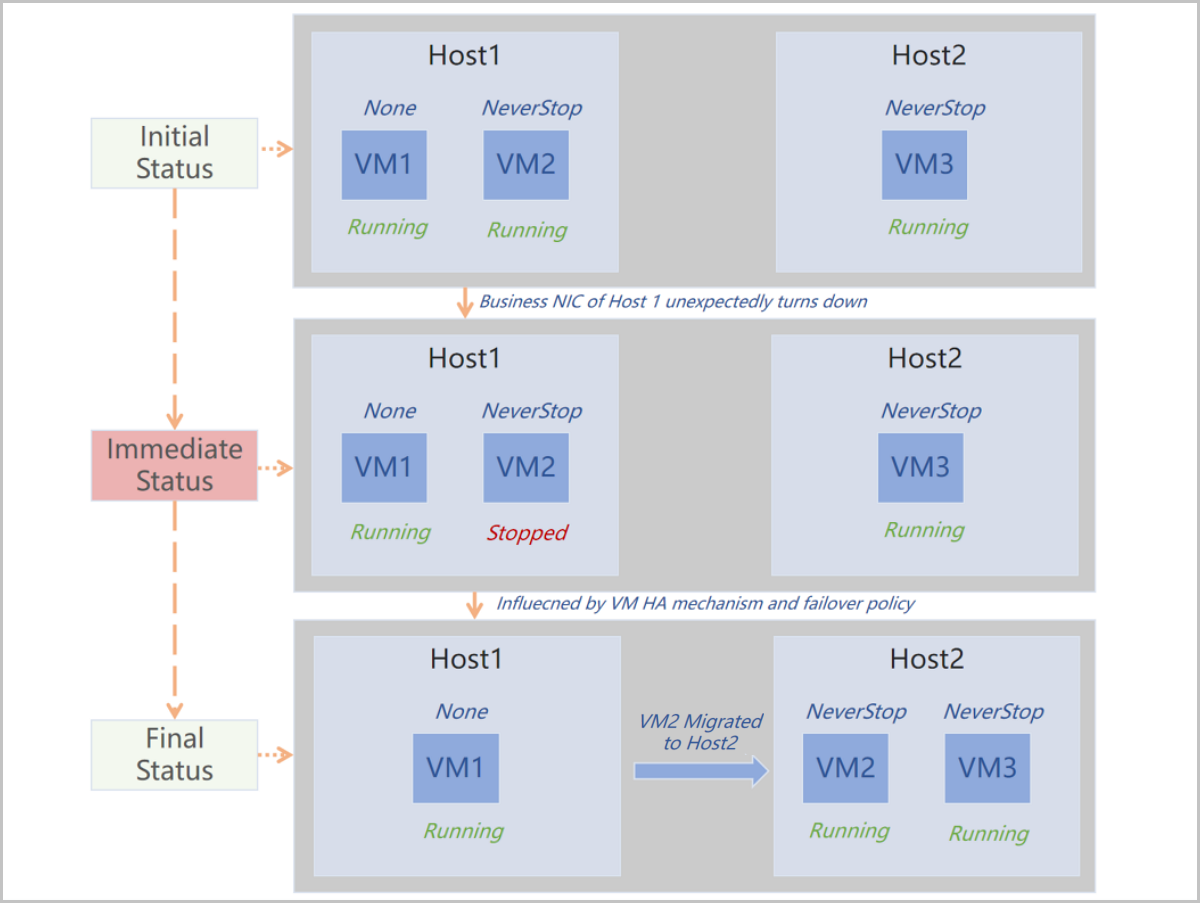
The following describes the scenarios of the HA Policy feature.
On the main menu of ZStack Cloud, choose . Then, the HA Policy page is displayed.
| Action | Description |
|---|---|
| Enable HA Policy | Enables the HA Policy feature. |
| Disable HA Policy | Disables the HA Policy feature. Note: If you disable HA Policy, VM instances will not be auto restarted if they are stopped. This may cause business interruptions. Proceed with caution. Note: If you disable HA Policy, VM instances will not be auto restarted if they are stopped. This may cause business interruptions. Proceed with caution. |
| Fault Scenario | Management Network Connectivity Status | Storage Network Connectivity Status | Business NIC Status | Fail Over |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Scenario A: Business NIC Fault | Normal | Normal | Abnormal | Enable/Disable |
| Scenario B: Storage Network Fault | Normal | Abnormal | Normal | Enable/Disable Note: If the storage type is SharedBlock and this status is Abnormal, VM instances will auto fail over regardless of this configuration. Note: If the storage type is SharedBlock and this status is Abnormal, VM instances will auto fail over regardless of this configuration. |
| Scenarios C: Storage Network and Business NIC Fault | Normal | Abnormal | Abnormal | Set as false if both the scenario A and B have the failover policy set as false. Set as true if either of the scenario A or B has the failover policy set as true. |
| Scenario D: Management Network Fault | Abnormal | Normal | Normal | Disable. The failover cannot be enabled in this scenario. |
 Note:
Note: | Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Host Self-Inspection Interval | The interval that a host inspects its own status. Default: 5. Unit: second. |
| Maximum Host Self-Inspection Attempts | The maximum number of attempts that a host inspects its own status. If the self-inspection of a host fails by the maximum attempts, it is determined that network errors occur with the host. Default: 6. |
| Category | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| VM Instance | VM Cross-Cluster HA | Specifies whether to enable VM migration across clusters to achieve high availability. Default: false. If set to true, hosts across clusters can be detected to achieve VM high availability.  Note: Note:
|
| Maximum Interval for VM Attempt to HA Start | The maximum interval for the system to finish the GC (garbage collection) job and attempt to restart a NeverStop VM according to the HA policy after the VM instance is stopped unexpectedly. Default: 300. Unit: second. | |
| VM Retry HA Start Interval | The interval for a Neverstop VM to retry an HA start after the previous HA start attempt fails. Default: 60. Unit: second. | |
| HA VM State Scanning Interval | The interval to scan the status of a NeverStop VM after it fails to HA start. Default: 60. Unit: second. | |
| HA VM State Update Speed | The speed of updating the state of NeverStop VM instances on the UI. Default: 1. Valid values: -1 to 5. A higher value indicates a lower update speed. However, a lower update speed makes the system ignore a lot of outdated notifications, thus decreasing the system workload. If set to -1, the NeverStop VM states on the UI are not updated automatically. | |
| VM HA Mode Default Value | Sets the default value of HA mode when creating VM instances. Valid values: None and NeverStop.
 Note: Note:
| |
| Host | Minimum Connection Attempts Required to Determine Host is Disconnected | The maximum times for the system to attempt to connect to a host. If the system fails to connect to the host after the specified times of attempt, the host is determined as disconnected. Default: 12. |
| Ping Response Time to Determine Host Connection is Established Successfully | The time period for the system to wait the host response after it pings the host. Receiving a response within this period indicates that the system establishes a successful connection with the host. Default: 5. Unit: second. | |
| Minimum Successful Connections Required to Determine Host is Re-Connected | The minimum successful connections that the system has to establish with a disconnected host before the host can be determined as re-connected. Default: 5. | |
| Timeout Period for Host Connecting to Primary Storage | The time for hosts to attempt to connect to primary storage. If a host fails to connect to a primary storage during this period, its connection attempt is determined as timeout. Default: 5. Unit: second. | |
| Minimum Connection Success Rate to Determine Host is Re-Connected | The minimum rate of successful connections occupied in total connection attempts to determine a disconnected host is successfully re-connected. Default: 50. Unit: %. | |
| Abnormal Host Status Update Interval | The interval for the system to check and update the status of abnormal hosts. Default: 5. Unit: second. |
On the main menu of ZStack Cloud, choose . Then, the HA Policy page is displayed. If HA policy is enabled and the HA mechanism is triggered, then HA logs are generated.
Back to Top
Email Us
contact@zstack.ioEmail Us
contact@zstack.ioEmail Us
contact@zstack.ioThe download link is sent to your email address.
If you don't see it, check your spam folder, subscription folder, or AD folder. After receiving the email, click the URL to download the documentation.Thank you for using ZStack products and services.
Submit successfully.
We'll connect soon.Thank you for using ZStack products and services.